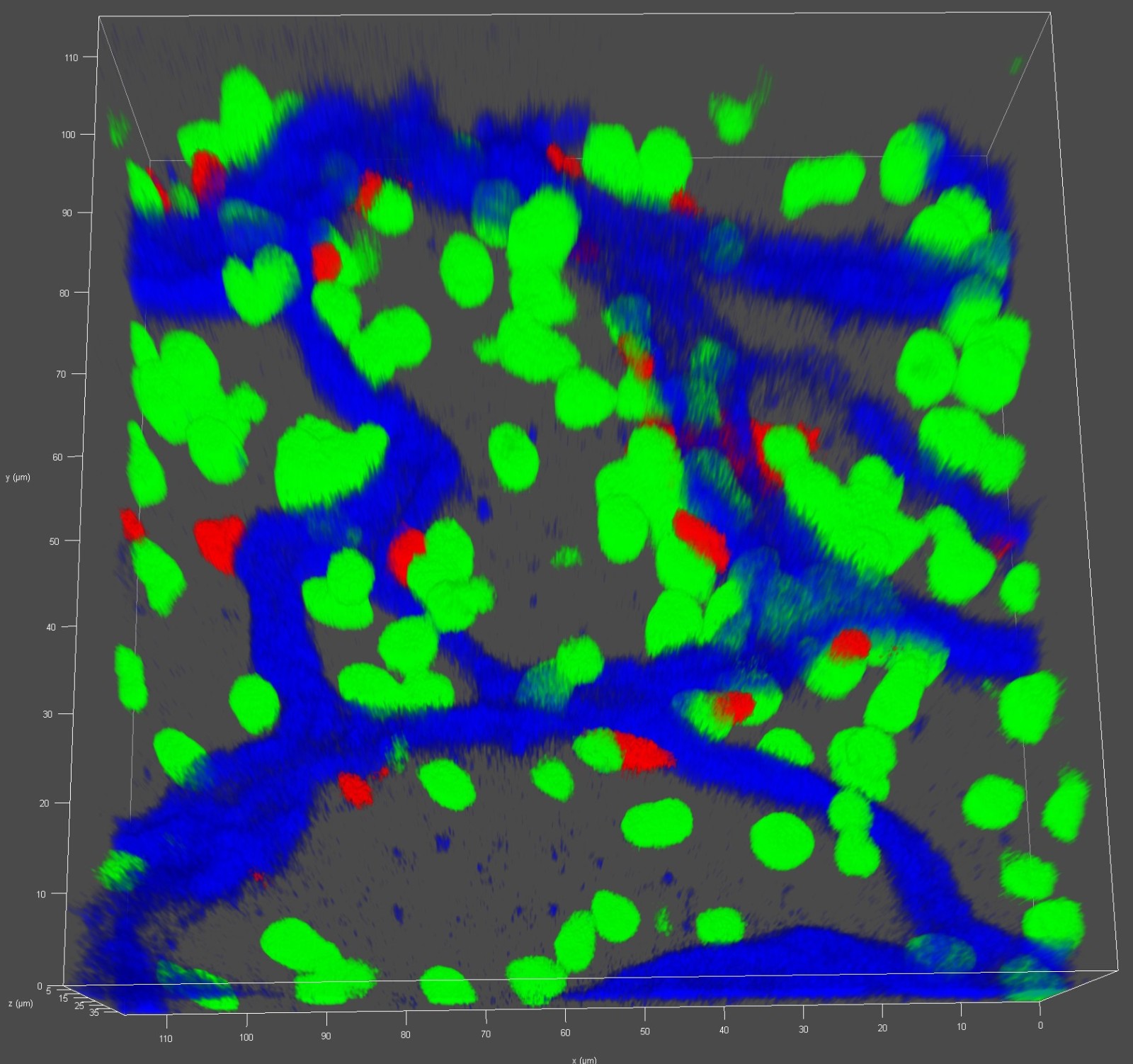
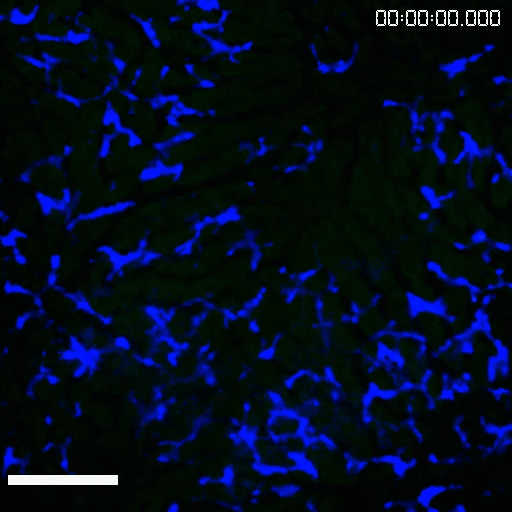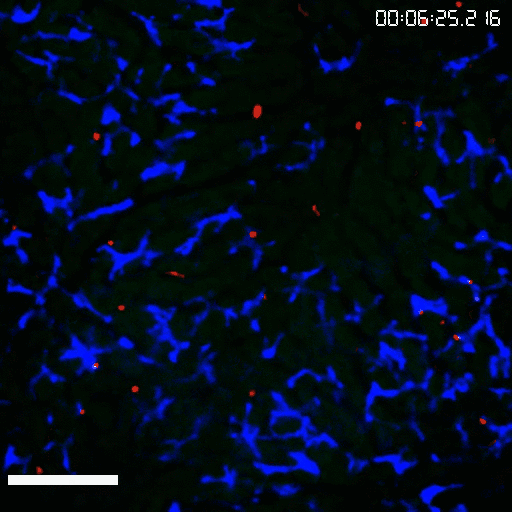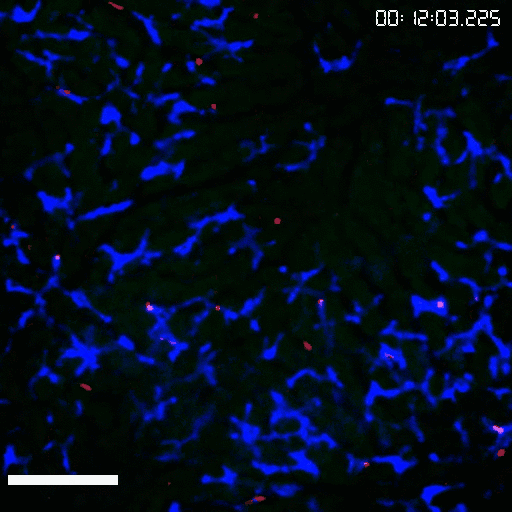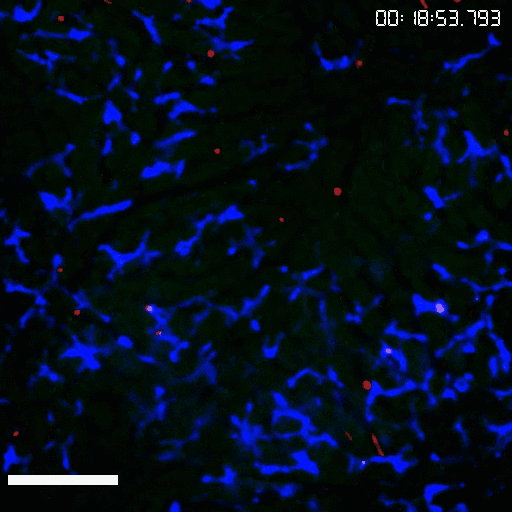
Kupffer cells is the largest tissue resident macrophage population in our entire body with an incredible ability to catch pathogens from the blood. Our previous work has proposed an unappreciated pattern recognition function of CRIg in Kupffer cell-mediated binding and capturing Gram-positive bacteria (Zeng Z. et al., Cell Host&Microbe, 2016). We also uncovered an estrogen-elicited natural antibody that was able to confer a fast capture of EPEC by Kupffer cells in females, partially explaining the sex-biased difference during bacterial infections and sepsis (Zeng Z. et al., Nat Immunol, 2018). By combining CRISPR mediated in vivo genome editing and intravital imaging, we are interested in identifying functional receptors expressed by tissue resident macrophages in promoting bacterial phagocytosis and in regulating T cell responses against pathogens during systemic and local infections.

邮编:
通讯/办公地址:
办公室电话:
版权所有 ©2020 图书馆VIP
地址:安徽省合肥市金寨路 96 号,邮政编码:230026
微信二维码